Managing network services and virtualization of network functions
Network services
Network services relay traffic over the network and apply network functions to it, such as WAN optimization, shaping, and traffic protection. Each network service has a topology that you build using a graphical design tool. You can add components to a topology and connect the components to each other.
You need to build a topology in a network service template and then assign that template to a tenant. Components added to the template topology are automatically assigned to the tenant together with the network service template. A tenant can create and deploy network services using assigned templates, and edit network services that are already deployed.
If you need to apply network functions from different network services to traffic, you can connect such network services to a shared network service.
You can use network services to deploy SD-WAN instances. Log into the self-service portal of the tenant for which you want to deploy an SD-WAN instance, create a network service, add control plane components to the topology of that network service, and deploy the network service. The network service for deploying SD-WAN instances is called the SD-WAN network service (SD-WAN service).
An example of a network service topology is shown in the figure below.
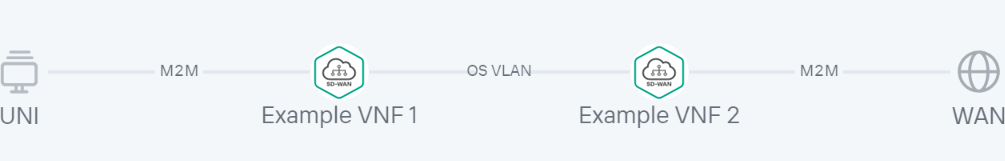
Network service topology
Network function virtualization
Network function virtualization (NFV) lets you use virtualized storage, compute resources, and networks to provide network functions and combine these functions into network services.
You can use virtual network functions (VNF) and physical network functions (PNF). The difference between virtual and physical network functions is that the physical network functions are deployed on dedicated hardware and do not use cloud resources.
Kaspersky SD-WAN complies with the architecture specified in the ETSI NFV MANO specification (NFV Management and Network Orchestration), which defines the following main functional components:
- Orchestrator.
- Virtual Network Function Managers (VNFM).
- Virtual Infrastructure Manager.
- The Zabbix monitoring system monitors the status of virtual and physical network functions and notifies the orchestrator when a network function needs to be restored or scaled.
- The NFV infrastructure consists of physical resources such as hardware storage, servers, and network devices.
- SD-WAN Controller.
The figure below shows the relations between the solution components and the NFV infrastructure. Components of external solutions are marked in white, Kaspersky SD-WAN components are marked in green, and the red lines are connections between components.
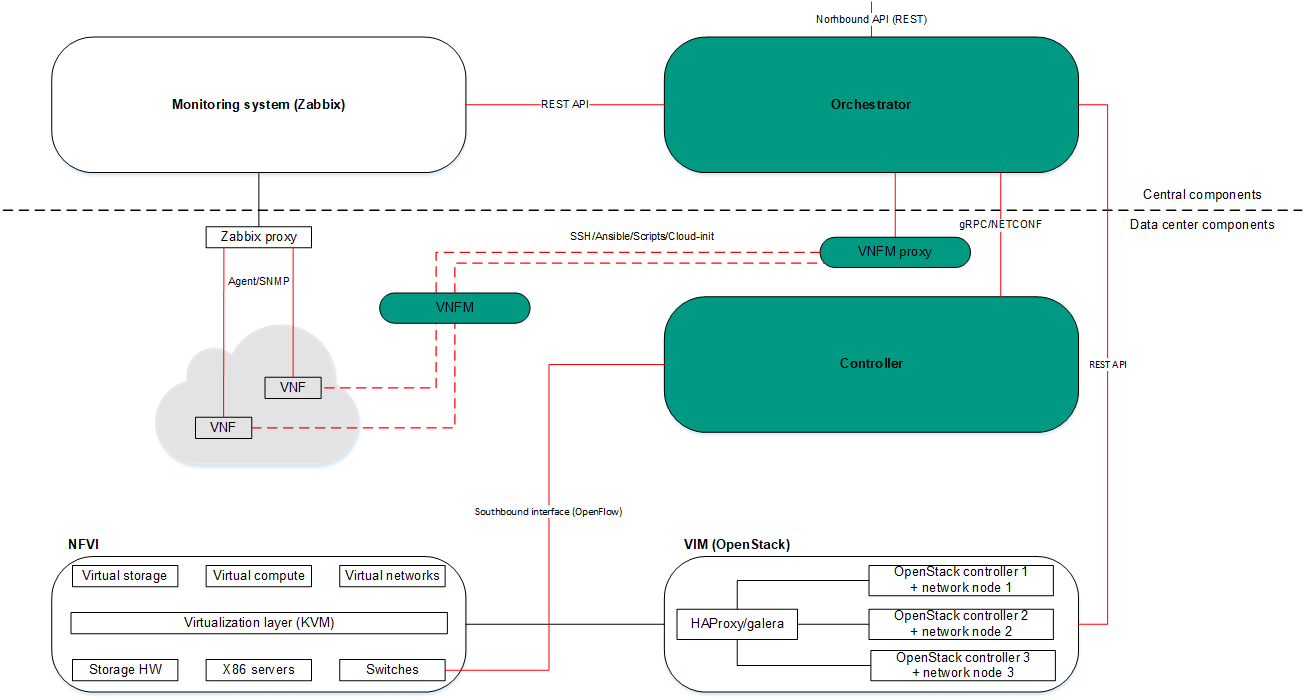
NFV infrastructure
